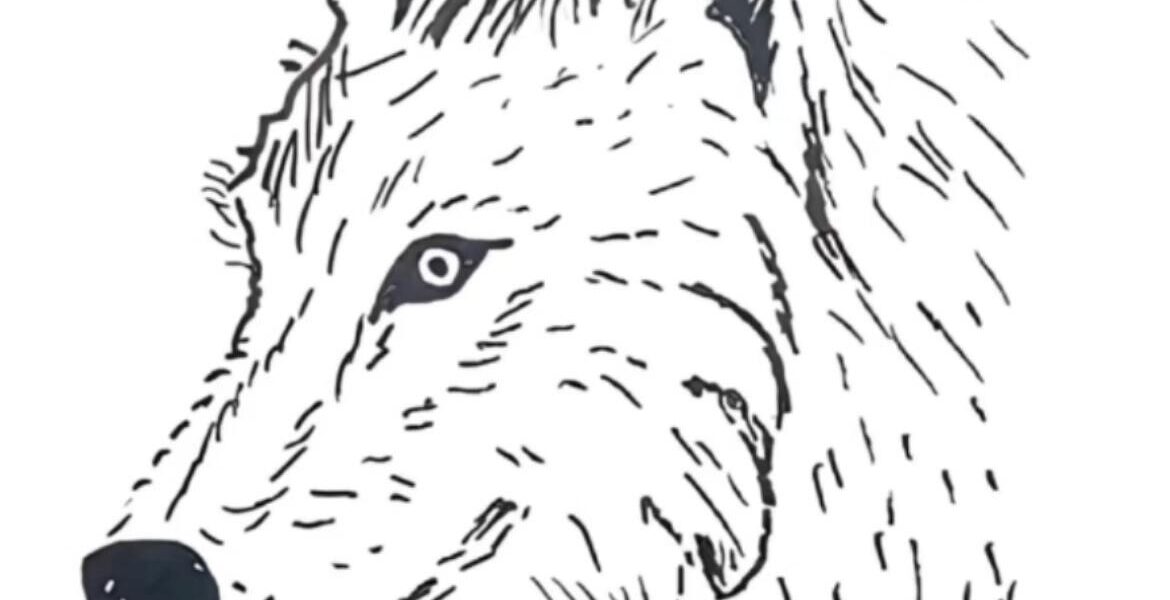
The Majesty and Mystery of Wolves: Understanding the Iconic Canine of the Wild
Wolves have long fascinated humans, symbolizing both the wildness of nature and the complex social bonds found within animal communities. The striking black-and-white sketch of a wolf’s head, with its intense gaze and detailed fur, perfectly captures the essence of this iconic creature—both fierce and intelligent.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the captivating world of wolves, their behavior, ecological importance, and the enduring cultural significance that keeps these animals deeply embedded in our imaginations.
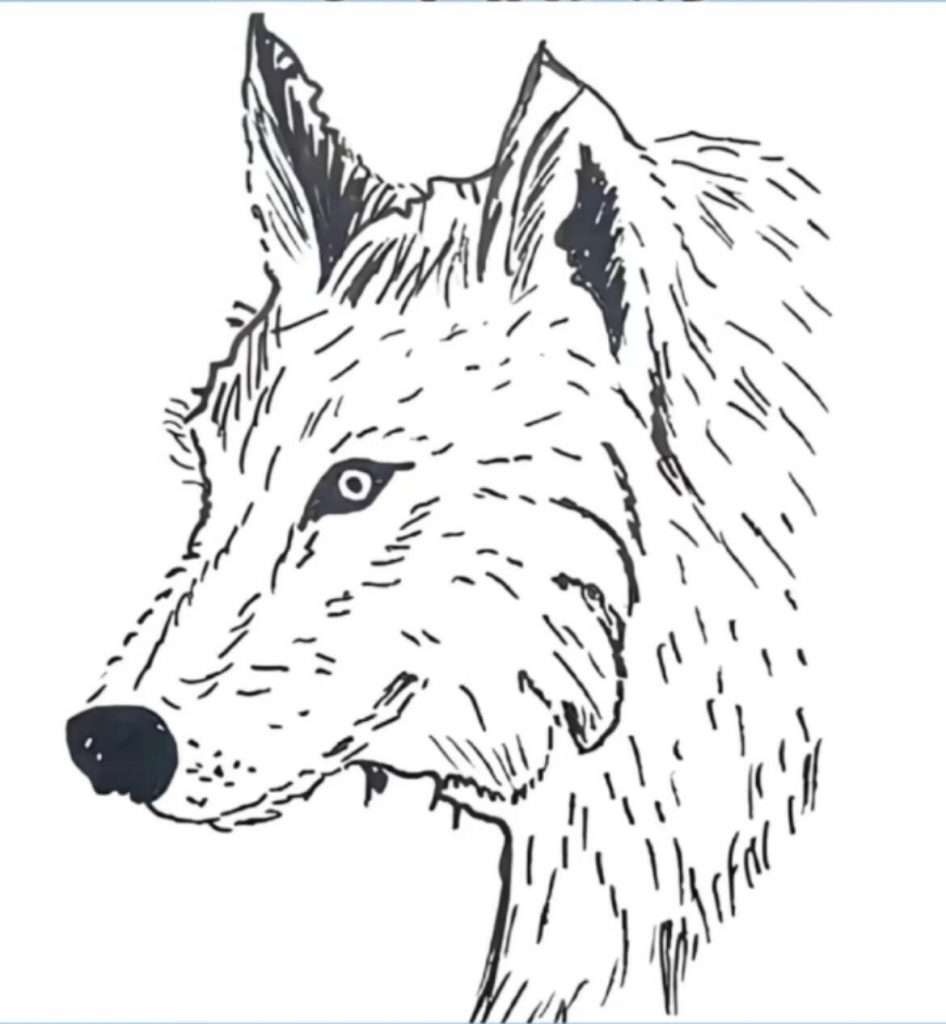

The Anatomy of a Wolf: More Than Just a Beautiful Face
The detailed sketch highlights key features that make wolves unique:
- Sharp Eyes: Wolves have keen eyesight that helps them hunt and communicate.
- Thick Fur: Their dense coat protects against harsh weather and blends with their surroundings.
- Strong Ears and Snout: Vital for hearing distant sounds and picking up scents, these features make wolves expert trackers.
Understanding these physical traits reveals how wolves are perfectly adapted to survive in diverse habitats.
Social Structure: The Pack Mentality
Wolves are known for their complex social structures. Living in packs allows them to:
- Coordinate Hunts: Working together increases success rates.
- Protect Territory: Packs defend their home ranges from rivals.
- Raise Young: Cooperative care helps pups survive and learn essential skills.
The pack is a family unit with clear hierarchies, emphasizing communication, loyalty, and cooperation.

Wolves in Ecosystems: The Balance Keepers
Wolves play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance:
- Regulate Prey Populations: By hunting herbivores like deer and elk, wolves prevent overgrazing.
- Promote Biodiversity: Their presence influences the behavior of other species, supporting healthier forests and grasslands.
- Scavenger Support: Leftover kills provide food for smaller animals.
Recognizing wolves as keystone species helps underline their importance in environmental conservation.
Understanding the Wolf: Anatomy and Adaptations
At first glance, the sketch reveals the wolf’s sharp eyes, keen ears, and dense fur—all perfectly adapted for survival in harsh environments. Let’s break down some key features:
- Eyes: Wolves have excellent night vision and a keen sense of movement, allowing them to detect prey from great distances.
- Fur: Their thick double coat insulates them against cold winters and blends with the landscape for camouflage.
- Ears and Nose: Exceptional hearing and a highly developed sense of smell help wolves detect prey and communicate with pack members over miles.
- Strong Jaws and Teeth: Designed for gripping and tearing meat, their dental structure reflects their carnivorous diet.
These adaptations highlight the wolf’s role as a top predator finely tuned to its ecosystem.

Cultural Significance: Wolves in Myth and Media
Throughout history, wolves have been revered and feared:
- Mythology and Folklore: Tales portray wolves as symbols of strength, cunning, or danger.
- Modern Media: Movies and books often depict wolves as noble heroes or mysterious loners.
- Spiritual Symbolism: Many cultures view wolves as guides or protectors.
This duality in perception reflects our complex relationship with nature’s wildest creatures.
Conservation Challenges: Protecting the Wolf
Despite their importance, wolves face numerous threats:
- Habitat Loss: Expanding human development reduces their living space.
- Human Conflict: Wolves sometimes come into conflict with livestock farmers.
- Poaching and Hunting: Illegal killings still occur despite protections.
Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration, legal protections, and education to foster coexistence.

How to Appreciate Wolves Responsibly
If you’re lucky enough to observe wolves in the wild, remember:
- Keep a Safe Distance: Avoid disturbing their natural behavior.
- Support Conservation: Donate or volunteer with wildlife organizations.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Spread awareness about the vital role wolves play.
Respecting these animals ensures they remain part of our world for generations.
Wolves in Human Culture: Myth, Symbolism, and Reality
Throughout history, wolves have occupied a powerful place in human culture:
- Mythology and Folklore: Seen as both noble guides and dangerous beasts, wolves appear in countless legends worldwide—from Roman mythology to Native American traditions.
- Literature and Media: Wolves are often portrayed as symbols of freedom, mystery, or even villains, reflecting our complex relationship with the wild.
- Spiritual Symbolism: Many cultures view wolves as totems representing loyalty, courage, and intuition.
These stories reveal how wolves resonate deeply within the human psyche, inspiring awe and sometimes fear.
Conclusion: Embracing the Spirit of the Wolf
The powerful sketch of the wolf’s head reminds us of the beauty, intelligence, and mystery embodied by these magnificent animals. They are not just creatures of the wild but vital components of our planet’s health and symbols that inspire us to appreciate the natural world more deeply.
By learning about wolves and supporting their protection, we celebrate the wild spirit that connects all life—and ensure that the howl of the wolf continues to echo through forests and mountains for years to come.




